Tenth Child Dies in UK as Whooping Cough Cases Continue to Rise
Whooping cough is a highly infectious ailment.
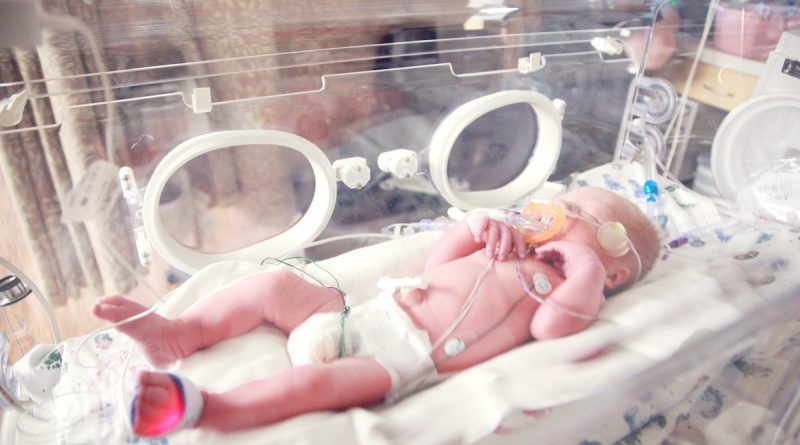
Yet another infant has perished from an infection of whooping cough, resulting in the total number of infant demises in England since the eruption began to 10, as specified by officials at the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA).
This fatality coincides with recent UKHSA data indicating that confirmed laboratory occurrences of whooping cough in England surpassed 10,000 this year. While the majority of instances are in individuals aged 15 or older, over 300 have been in babies under three months – the most vulnerable group to the ailment.
It is speculated that the eruption commenced in England last November, with now 10 infant fatalities officially confirmed. The initial demise was documented in December 2023, with the remaining transpiring between January and June 2024.
As per a Bloomberg report, Whooping cough is resurging in various regions of the globe, with fatalities reported in China, the Philippines, Czech Republic, and the Netherlands, and outbreaks in nations including the US and UK.
What is whooping cough?
The highly infectious ailment is triggered by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis, which targets the upper respiratory system, releasing toxins that can provoke the airways to swell, as per the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What are the symptoms?
Initial symptoms of whooping cough bear a striking resemblance to the common cold – with a congested nose, mild fever, and a gentle cough frequently reported. This makes it challenging to diagnose until more severe symptoms manifest.
Following a week or two, symptoms can advance to “swift, violent, and uncontrolled coughing fits,” according to the CDC, accompanied by a high-pitched “whoop” sound upon inhalation at the conclusion of the fit. Coughing fits can persist for up to 10 weeks.
Who is most at risk?
Children are more prone to experience the most intense symptoms of whooping cough, while infants typically do not cough but can cease breathing. Adolescents and adults frequently exhibit milder symptoms, yet even then, incapacitating coughing fits can prevent them from sleeping at night. One complicating element is that adults with no apparent indications of the ailment can continue to spread the infection.
How do you manage it?
Upon diagnosis, ideally before coughing commences, physicians typically manage the infection with antibiotics. If a patient has been coughing for over three weeks, antibiotics are unnecessary as the bacteria likely departed the body and the coughing is a consequence of damage inflicted on the airways.
Is there a whooping cough vaccine?
In China, complimentary vaccines are usually administered in a combined injection that also shields infants against diphtheria and tetanus. In the US, two vaccines are accessible – one for children below seven years old, and one for individuals older than seven. In the UK, injections are regularly given to infants, while the Philippines has cautioned of a potential scarcity in supply by May.
Awaiting response to load…