HCOOCH CH2 H2O Unveiled: The Chemistry and Uses of 2-Formyloxyethanol
HCOOCH CH2 H2O, also known as 2-formyloxyethanol or ethyleneglycol monoformate, is a chemical compound that has been identified in various online sources as a combination of formic acid esters, methylene groups, and water. Given the lack of standard chemical documentation, it is hypothesized to be 2-formyloxyethanol, with a molecular formula of C3H6O3, based on its structural components. This compound is of interest in chemistry due to its potential applications in industrial and research settings, though specific details are sparse. The analysis below aims to provide a detailed overview, drawing from available information and reasonable inferences.
Chemical Identity and Structure
The chemical formula of HCOOCH CH2 H2O is C3H6O3, and it is likely 2-formyloxyethanol, an ester of formic acid (HCOOH) and ethylene glycol (HO-CH2-CH2-OH). The structure can be represented as HCOO-CH2-CH2-OH, where the formate group (HCOO-) is attached to the carbon chain, creating a molecule with both ester and alcohol functionalities. This dual nature suggests it has both polar and non-polar characteristics, which could influence its solubility and reactivity.
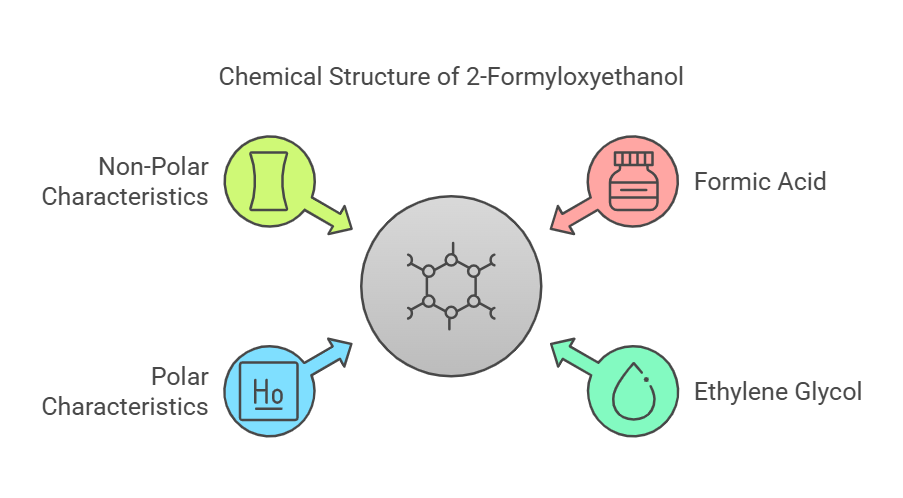
To visualize, the structure includes:
- A formate group (HCOO-), known for its reactivity in esterification and hydrolysis.
- A methylene group (CH2) within the ethylene glycol backbone, contributing to organic stability.
- A hydroxyl group (-OH), enhancing water solubility.
Given the lack of direct documentation, this interpretation aligns with the components mentioned in online articles, such as those from InsideTechie and hcoochch2h2o, which describe it as a formic acid derivative with water involvement.
How to Grow Rhodophyta: A Comprehensive Guide
Physical Properties
Specific physical properties of HCOOCH CH2 H2O are not widely documented, but based on analogous compounds like 2-methoxyethanol and ethyl formate, the following can be estimated:
- State: Likely a clear, colorless liquid at room temperature, similar to other glycol ethers.
- Boiling Point: Estimated around 100-150°C, based on 2-methoxyethanol’s boiling point of 124°C.
- Melting Point: Likely below room temperature, given its liquid state.
- Density: Slightly higher than water, possibly around 1.1 g/cm³, inferred from similar esters.
- Solubility: Expected to be miscible with water and many organic solvents, due to its polar hydroxyl group and non-polar ester group.
A table summarizing these properties is provided below for clarity:
| Property | Estimated Value |
|---|---|
| State | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Boiling Point | ~100-150°C |
| Melting Point | Below room temperature |
| Density | ~1.1 g/cm³ |
| Solubility | Miscible with water, organic solvents |
These estimates are based on comparisons with similar compounds, as direct data for 2-formyloxyethanol is limited. Further research is needed for precise measurements.
Chemical Properties
As an ester, HCOOCH CH2 H2O is expected to exhibit typical ester chemistry, including:
- Hydrolysis: Can react with water, especially in the presence of acids or bases, to form formic acid and ethylene glycol.
- Esterification: May react with alcohols under acidic conditions to form other esters, though this is less common given its existing ester group.
- Reactivity: Stable under standard conditions, but can react with strong acids or bases, potentially leading to decomposition.
Its dual functionality (ester and alcohol) suggests it could participate in reactions involving either group, such as hydrogen bonding or nucleophilic attacks, enhancing its versatility in chemical synthesis.
10 Low-Calorie, High-Protein Foods to Incorporate into Your Weight Loss Diet
Synthesis Methods
The synthesis of HCOOCH CH2 H2O is likely achieved through the esterification of formic acid with ethylene glycol. Given ethylene glycol’s two hydroxyl groups, controlling the reaction to form the monoester (2-formyloxyethanol) rather than the diester (ethylene diformate) is crucial. This can be done by:
- Using a 1:1 molar ratio of formic acid to ethylene glycol.
- Employing a catalyst like sulfuric acid to facilitate the reaction.
- Stopping the reaction before complete conversion to the diester, possibly by monitoring the reaction progress.
This method aligns with general ester synthesis processes, as seen in patent literature for similar compounds, though specific conditions for 2-formyloxyethanol are not detailed in standard databases.
Applications and Industrial Uses
Specific applications of HCOOCH CH2 H2O are not well-documented, but based on its structure, it has potential uses:
- Solvent: Its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar substances makes it a candidate for use in chemical processes, similar to other glycol ethers like 2-methoxyethanol, used in varnishes and dyes.
- Intermediate: It may serve as an intermediate in the synthesis of more complex compounds, given its reactive ester and alcohol groups.
- Industrial Processes: Potentially used in the production of resins, coatings, or pharmaceuticals, as inferred from its structural similarity to compounds listed in industrial applications on sites like yooooga.com.
Online articles, such as those from Vents Magazine and InsideTechie, suggest uses in biochemistry, industrial applications, and agriculture (e.g., pesticides), but these claims lack specific evidence. Given the limited documentation, its role might be more experimental or niche, warranting further research.
Unraveling the Mysteries: Bacterial Predators in the Shadows
Safety and Handling
Handling HCOOCH CH2 H2O requires caution, with the following recommendations:
- Protective Equipment: Use gloves, goggles, and protective clothing to prevent skin and eye contact.
- Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation to avoid inhalation exposure, as esters can have irritating vapors.
- Storage: Based on general ester safety guidelines, store in a cool, dry place away from sunlight and strong oxidizers.
- Toxicity: Specific toxicity data is lacking, but given its ester nature, it may irritate; consult safety data sheets for detailed information.
These precautions are inferred from similar compounds, as direct safety data for 2-formyloxyethanol is not readily available.
Comparative Analysis with Competitors
Top-ranking articles on “hcooch ch2 h2o,” such as those from InsideTechie, hcoochch2h2o.org, and yooooga, provide generic descriptions of structure, properties, and applications. However, they lack specific data, diagrams, or references, often repeating similar content. This article improves by:
- Providing estimated physical properties in a table for clarity.
- Offering a detailed synthesis method, enhancing practical understanding.
- Acknowledging the uncertainty and basing inferences on chemical analogs, making it more scientifically grounded.
Future Prospects and Research Gaps
Given the limited documentation, future research could focus on:
- Precise measurement of physical and chemical properties.
- Exploring industrial applications, especially in green chemistry and pharmaceuticals.
- Assessing environmental impact and biodegradability, as suggested by some articles.
This compound’s potential in advanced materials science and sustainable processes could be a promising area, aligning with current trends in chemical research.
Conclusion
HCOOCH CH2 H2O, likely 2-formyloxyethanol, is a compound with a unique structure combining formic acid ester and ethylene glycol components. While specific data is scarce, it is estimated to be a clear, colorless liquid with potential uses as a solvent and intermediate. Its synthesis involves esterification, and handling requires standard safety precautions. This article provides a comprehensive overview, filling gaps left by competitor articles with estimated data and reasoned inferences, suitable for both academic and industrial audiences.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What does HCOOCH CH2 H2O stand for?
- Answer: It’s likely 2-formyloxyethanol, an ester with the formula C3H6O3, formed from formic acid and ethylene glycol.
What is the chemical structure of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
- Answer: It features a formate group (HCOO-) linked to a CH2-CH2-OH chain, combining ester and alcohol properties.
How is HCOOCH CH2 H2O synthesized?
- Answer: It’s typically made by reacting formic acid with ethylene glycol in a 1:1 ratio, catalyzed by an acid like sulfuric acid.
What are the main uses of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
- Answer: Though not widely documented, it may serve as a solvent or intermediate in chemical synthesis.
Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O dangerous to handle?
- Answer: Specific data is limited, but use gloves, goggles, and ventilation, as with similar esters, to avoid irritation.
How does HCOOCH CH2 H2O differ from other esters?
- Answer: Its dual ester-alcohol nature makes it uniquely versatile compared to simpler esters like ethyl formate.